Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, commonly known as COPD, is a debilitating respiratory condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterised by persistent respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation, COPD significantly impacts the quality of life of those diagnosed with it. But beyond the physical and emotional toll, there’s a substantial financial burden associated with managing this chronic illness. Whether you’re a patient, a caregiver, or a healthcare professional, understanding the various costs associated with COPD is crucial.
Why is it important to delve into the costs of COPD? For starters, it helps patients and families prepare for the financial impact, allowing them to make informed decisions about treatment and care. Additionally, it sheds light on the economic strain placed on healthcare systems and society at large. From direct medical expenses to the indirect costs that ripple through families and communities, the financial implications of COPD are far-reaching and complex. In this article, we’ll explore these costs in detail, offering insights and practical advice for managing them effectively.
So, what exactly does it cost to live with and manage COPD? Let’s dive in and break it down step by step.
The Medical Costs of COPD
Direct Medical Costs
The most immediate and apparent costs of COPD are the direct medical expenses. These include hospitalisations, emergency visits, medications, and treatments specifically related to managing the disease.
Hospitalisation and Emergency Visits
Hospitalisations are a significant component of the direct medical costs associated with COPD. Exacerbations, or flare-ups of symptoms, often necessitate emergency room visits and extended hospital stays. These events are not only physically taxing for patients but also financially draining. The cost of a single hospitalisation can run into thousands of pounds, depending on the severity of the episode and the level of care required.
Medications and Treatments
Medications form a cornerstone of COPD management. From bronchodilators and corticosteroids to antibiotics and supplemental oxygen, the list of necessary drugs can be extensive. The cost of these medications can add up quickly, especially for patients who require multiple prescriptions. Furthermore, treatments such as pulmonary rehabilitation and routine follow-up appointments with specialists contribute to the overall medical expenses.
Indirect Medical Costs
Beyond the direct costs, COPD also incurs substantial indirect medical expenses. These are often less visible but equally impactful on the patient’s finances.
Long-term Care
As COPD progresses, many patients require long-term care, which can include home healthcare services, assisted living facilities, or nursing home care. These services provide critical support but come at a high cost, often not fully covered by insurance or public health programs.
Rehabilitation Services
Rehabilitation services, particularly pulmonary rehabilitation, are vital for maintaining lung function and overall health in COPD patients. While these programs offer significant benefits, they also represent an additional financial burden, especially if ongoing participation is required.
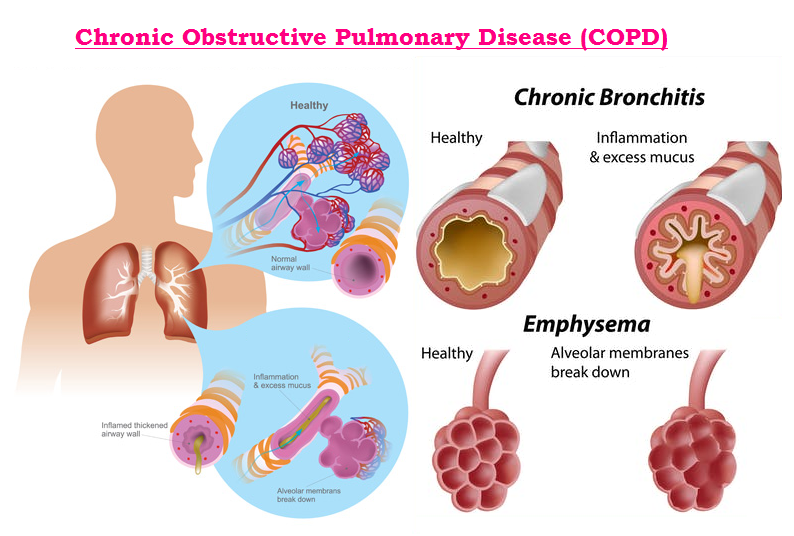
Economic Burden on Patients and Families
Out-of-Pocket Expenses
Out-of-pocket expenses are a significant concern for COPD patients and their families. These costs include anything not covered by insurance, which can be substantial.
Prescription Costs
Even with insurance, the cost of prescriptions can be a heavy burden. Co-pays, deductibles, and non-covered medications add up, often leading to difficult financial decisions for patients.
Regular Doctor Visits
Frequent visits to doctors, including specialists like pulmonologists, are necessary to manage COPD effectively. These appointments, along with diagnostic tests and procedures, can strain a family’s budget.
Loss of Income
COPD not only affects physical health but also impacts a patient’s ability to work, leading to loss of income and financial instability.
Inability to Work
Many COPD patients find it challenging to maintain full-time employment due to their symptoms. Breathlessness, fatigue, and frequent exacerbations make it difficult to perform job duties, resulting in reduced hours or job loss.
Disability Benefits
While disability benefits provide some financial relief, they often fall short of replacing a full income. The process of securing these benefits can be complex and time-consuming, adding to the stress experienced by patients and their families.
Impact on the Healthcare System
Healthcare Resource Utilisation
COPD places a significant demand on healthcare resources, affecting hospitals, clinics, and the broader healthcare infrastructure.
Strain on Hospitals and Clinics
The frequent need for hospitalisations and emergency care for COPD exacerbations strains hospital resources. This demand affects not only bed availability but also the workload of healthcare providers.
Healthcare Staffing Challenges
Managing COPD requires a multidisciplinary approach, involving pulmonologists, respiratory therapists, and other specialists. The growing number of COPD patients can lead to staffing challenges, impacting the quality of care provided.
Public Health Costs
The economic burden of COPD extends to public health systems, influencing government spending and insurance premiums.
Government Expenditures
Governments incur substantial costs related to COPD through public health programs, Medicare, and Medicaid. These expenditures cover hospital stays, treatments, and long-term care, representing a significant portion of healthcare budgets.
Insurance Implications
Insurance companies also bear the financial burden of COPD, leading to higher premiums for policyholders. The increased costs associated with COPD care contribute to the overall rise in healthcare costs, affecting everyone within the system.
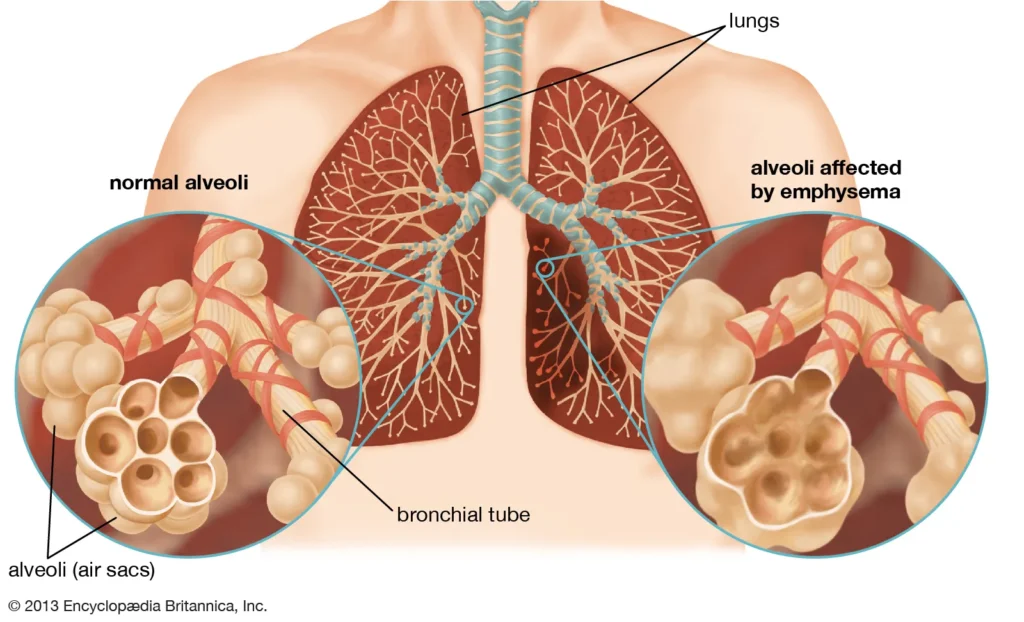
The Psychological Costs of COPD
Mental Health Impact
Living with COPD can take a severe toll on mental health, contributing to anxiety, depression, and other psychological issues.
Anxiety and Depression
COPD patients often experience anxiety and depression due to the chronic nature of the disease and its impact on their daily lives. The fear of exacerbations and the limitations imposed by breathlessness contribute to these mental health challenges.
Coping Mechanisms
Effective coping mechanisms, such as counselling and support groups, are essential for managing the psychological impact of COPD. However, accessing these resources can incur additional costs, adding to the overall burden.
Social Isolation
COPD can lead to social isolation, further exacerbating the psychological impact of the disease.
Impact on Relationships
The limitations imposed by COPD can strain relationships with family and friends. Social activities may become challenging, leading to a sense of isolation and loneliness.
Community Support Systems
Community support systems, including local support groups and online communities, play a crucial role in helping COPD patients stay connected. These resources provide emotional support and practical advice, although participation may involve additional expenses.
Prevention and Management of COPD
Preventative Measures
Preventing COPD or slowing its progression can significantly reduce costs and improve quality of life.
Smoking Cessation
Smoking is the leading cause of COPD. Smoking cessation programs, including nicotine replacement therapies and counselling, are essential in preventing COPD. While these programs involve upfront costs, they can save substantial amounts in long-term healthcare expenses.
Environmental Factors
Reducing exposure to environmental pollutants, such as industrial emissions and indoor air pollutants, can also help prevent COPD. Implementing measures to improve air quality can have long-term health benefits and reduce medical costs.
Effective Management Strategies
Managing COPD effectively involves a combination of medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and ongoing support.
Pulmonary Rehabilitation
Pulmonary rehabilitation programs offer comprehensive support, including exercise training, nutritional advice, and education. These programs help patients manage symptoms and improve their quality of life, although they represent an additional financial commitment.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy diet, staying active, and avoiding respiratory irritants, are crucial for managing COPD. These changes can reduce symptoms and the need for medical interventions, leading to cost savings over time.
Advances in COPD Treatment
New Medications
Innovations in COPD treatment are continually emerging, offering new hope for patients.
Innovative Drug Therapies
New drug therapies are being developed to target COPD symptoms more effectively. These medications can improve lung function and reduce exacerbations, although their cost and accessibility remain concerns.
Access and Affordability
Ensuring access to these innovative treatments is crucial. Policies to make these medications affordable and available to all patients can help mitigate the economic burden of COPD.
Technological Innovations
Technology is playing an increasingly important role in managing COPD, providing new tools for patients and healthcare providers.
Telemedicine
Telemedicine offers a convenient and cost-effective way for COPD patients to consult with healthcare providers. Remote consultations can reduce the need for in-person visits, saving time and money.
Remote Monitoring Devices
Remote monitoring devices, such as smart inhalers and wearable sensors, help track symptoms and medication usage. These technologies provide valuable data for managing COPD and can alert healthcare providers to potential issues before they become serious.
Policy and Advocacy
Government Policies
Effective government policies are essential for addressing the challenges posed by COPD.
Health Policy Reforms
Health policy reforms that prioritise COPD prevention, research, and treatment can significantly impact the economic burden of the disease. Funding for public health initiatives and research into new treatments is vital.
Funding for COPD Research
Increased funding for COPD research can lead to breakthroughs in understanding and treating the disease. Research into new therapies, early detection methods, and prevention strategies can reduce the long-term costs associated with COPD.
Advocacy Efforts
Advocacy efforts play a critical role in raising awareness and securing support for COPD patients.
Patient Advocacy Groups
Patient advocacy groups work tirelessly to support those affected by COPD. These organisations provide resources, lobby for policy changes, and raise public awareness about the disease.
Raising Awareness
Raising awareness about COPD is crucial for securing funding, improving patient care, and reducing stigma. Public health campaigns and educational initiatives can inform the public about COPD, its impact, and the importance of early intervention.
Support Systems and Resources
Patient Support Networks
Strong support networks are vital for COPD patients, offering emotional and practical assistance.
Online Communities
Online communities provide a platform for COPD patients to connect, share experiences, and offer support. These virtual networks can be a lifeline for those feeling isolated by their condition.
Support Groups
In-person support groups offer a space for patients to discuss their challenges and successes. These groups provide valuable social interaction and emotional support, helping patients cope with their disease.
Educational Resources
Access to accurate and comprehensive educational resources is essential for patients and caregivers.
Information for Patients and Caregivers
Providing patients and caregivers with detailed information about COPD helps them make informed decisions about treatment and management. Educational materials, workshops, and counselling services are invaluable resources.
Training for Healthcare Providers
Training for healthcare providers ensures they have the knowledge and skills to offer the best care for COPD patients. Continuous education and professional development opportunities help healthcare workers stay updated on the latest treatments and management strategies.
Conclusion
Understanding the costs associated with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is crucial for patients, families, and healthcare systems. From direct medical expenses and indirect costs to the psychological impact and economic burden on society, COPD presents significant challenges. However, with effective prevention, management strategies, and advances in treatment, it is possible to alleviate some of these financial burdens. Advocacy, support systems, and educational resources also play a vital role in improving the lives of those affected by COPD. By raising awareness and implementing comprehensive care plans, we can work towards a future where the costs of COPD are significantly reduced, and patients can lead healthier, more fulfilling lives.
Frequently Asked Questions?
What are the primary causes of COPD?
COPD is primarily caused by long-term exposure to irritants that damage the lungs and airways, such as smoking, air pollution, and occupational dust and chemicals.
Can COPD be cured?
While there is no cure for COPD, effective management and treatment can help control symptoms and improve quality of life.
What lifestyle changes can help manage COPD?
Key lifestyle changes include quitting smoking, avoiding respiratory irritants, staying active, and following a healthy diet.
How does COPD impact mental health?
COPD can lead to anxiety, depression, and social isolation due to the chronic nature of the disease and its symptoms.
What are the latest advancements in COPD treatment?
Recent advancements include new drug therapies, telemedicine, and remote monitoring devices that help manage symptoms and improve patient care.
How can patients access support for COPD?
Patients can access support through online communities, in-person support groups, and patient advocacy organisations that provide resources and assistance.
What role do government policies play in managing COPD?
Government policies are crucial for funding research, implementing health policy reforms, and providing public health initiatives to prevent and manage COPD effectively.