Liver disease is a significant global health concern that affects millions of people worldwide. It’s like an undercurrent in the vast ocean of health issues, often going unnoticed until it becomes severe. The liver, a vital organ responsible for detoxification, protein synthesis, and digestion, can be affected by various conditions, each with its own set of challenges. From lifestyle-related issues to genetic disorders, liver disease encompasses a broad spectrum of ailments that require timely diagnosis and management.
Understanding the cost associated with liver disease isn’t just about the financial burden. It also involves considering the emotional and physical toll it takes on patients and their families. Diagnosing liver disease can be complex and expensive, involving various tests and procedures. Once diagnosed, managing the condition becomes a lifelong commitment, with costs accumulating over time. The financial implications can be overwhelming, especially for those without adequate insurance or access to healthcare services.
In this article, we’ll dive into the intricacies of liver disease, exploring its causes, symptoms, and diagnostic processes. We’ll then delve into the management and treatment options available, highlighting their associated costs. By the end, you’ll have a clearer understanding of the financial landscape surrounding liver disease and how it affects both individuals and society as a whole.
Understanding Liver Disease
The liver is a vital organ that plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health, acting as the body’s chemical processing plant. It’s involved in detoxification, protein synthesis, and digestion, to name just a few of its essential functions. Liver disease refers to any condition that affects the liver’s functionality and can manifest in various forms. Understanding these diseases is the first step in grasping the overall cost and impact they have on individuals and healthcare systems.
What is Liver Disease?
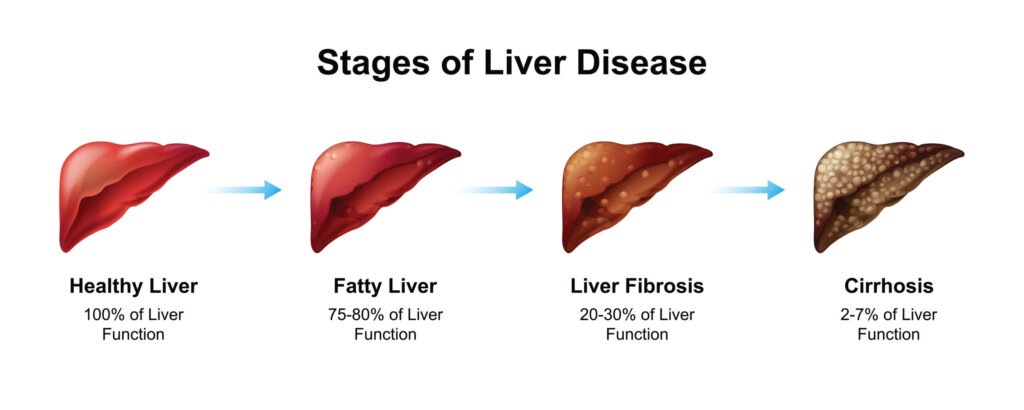
Liver disease encompasses a broad range of conditions that cause damage to the liver, impairing its ability to function properly. It can result from a variety of factors, including infections, genetic predispositions, and lifestyle choices. Essentially, any condition that leads to inflammation, injury, or scarring of the liver can be classified under the umbrella of liver disease.
The liver’s ability to regenerate is remarkable, but repeated or sustained damage can lead to chronic liver disease or cirrhosis. This progressive condition replaces healthy liver tissue with scar tissue, ultimately leading to liver failure if not managed effectively.
Common Types of Liver Disease
There are several types of liver disease, each with its own set of causes and implications:
- Hepatitis: This is an inflammation of the liver, commonly caused by viral infections (hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E). Hepatitis B and C are the most concerning as they can lead to chronic liver disease and increase the risk of liver cancer.
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): This condition is characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver of individuals who consume little or no alcohol. It is closely linked to obesity and metabolic syndrome.
- Alcoholic Liver Disease: As the name suggests, this disease is caused by excessive alcohol consumption, leading to liver inflammation and cirrhosis over time.
- Cirrhosis: Cirrhosis is the end stage of chronic liver disease, resulting from prolonged damage and scarring. It can be caused by various factors, including chronic viral hepatitis, alcohol abuse, and NAFLD.
- Liver Cancer: This can occur as a primary cancer originating in the liver or as a secondary cancer spreading from other parts of the body.
Understanding these conditions and their implications is crucial in assessing the cost of diagnosis and management.
Causes and Risk Factors
Liver disease can be caused by a myriad of factors, ranging from lifestyle choices to genetic predispositions. Recognising these causes is essential for both prevention and early intervention.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Lifestyle choices have a significant impact on liver health. Here are some key factors that contribute to liver disease:
- Alcohol Consumption: Excessive drinking is a major cause of liver disease, leading to conditions like alcoholic liver disease and cirrhosis. The liver metabolises alcohol, and excessive intake can overwhelm its capacity, causing damage.
- Obesity: Obesity is closely linked to NAFLD, where fat accumulates in the liver cells. This can progress to a more severe condition known as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), characterised by inflammation and liver damage.
- Diet and Nutrition: A poor diet high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats can contribute to liver damage. Conversely, a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can support liver health.
- Exposure to Toxins: Environmental toxins, such as industrial chemicals and pollutants, can harm the liver over time. Occupational exposure to such substances is a risk factor for liver disease.
- Drug Use: Certain medications and illicit drugs can be toxic to the liver, causing damage and impairing its function.
Genetic Predispositions
While lifestyle choices play a significant role, genetic factors can also contribute to liver disease:
- Hereditary Hemochromatosis: This genetic disorder causes excessive iron accumulation in the body, leading to liver damage and other complications.
- Wilson’s Disease: This rare genetic disorder leads to copper accumulation in the liver, causing liver and neurological damage.
- Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency: This genetic condition affects the liver and lungs, leading to liver disease in some individuals.
Understanding the causes and risk factors of liver disease is vital for both prevention and early intervention, as it allows individuals to make informed choices about their lifestyle and health.
Symptoms and Early Detection
Recognising the signs and symptoms of liver disease is crucial for early detection and intervention. The liver, being a resilient organ, often doesn’t show symptoms until significant damage has occurred. However, early detection can make a significant difference in the management and treatment of liver disease.
Recognising the Signs of Liver Disease
Liver disease can manifest with a wide range of symptoms, which can vary depending on the underlying cause and stage of the disease. Here are some common signs to watch out for:
- Jaundice: One of the hallmark signs of liver disease is jaundice, characterised by yellowing of the skin and eyes. This occurs due to the buildup of bilirubin, a yellow pigment, in the blood when the liver is unable to process it effectively.
- Fatigue: Persistent fatigue and weakness are common symptoms of liver disease, as the liver plays a vital role in energy metabolism.
- Abdominal Pain and Swelling: Pain or discomfort in the upper right abdomen, along with swelling, can indicate liver problems.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Digestive issues, including nausea and vomiting, can occur when the liver is not functioning optimally.
- Dark Urine and Pale Stools: Changes in urine and stool colour can be indicative of liver disease.
- Itchy Skin: Itchy skin, caused by the accumulation of bile salts, can be a symptom of liver dysfunction.
It’s important to note that these symptoms can also be associated with other health conditions, making it essential to seek medical evaluation for an accurate diagnosis.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis of liver disease is crucial for several reasons:
- Preventing Progression: Detecting liver disease at an early stage can help prevent its progression to more severe conditions like cirrhosis or liver cancer.
- Timely Intervention: Early diagnosis allows for timely intervention, which can significantly improve treatment outcomes and quality of life.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Early diagnosis provides an opportunity for individuals to make necessary lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthier diet, reducing alcohol consumption, and managing risk factors like obesity.
- Improved Prognosis: The earlier liver disease is detected and managed, the better the prognosis for the patient.
Regular health check-ups and screenings are essential, especially for individuals with risk factors for liver disease. Early detection can be life-saving and can significantly reduce the overall cost of treatment.
Diagnosis of Liver Disease
The diagnosis of liver disease involves a combination of medical tests and procedures to assess liver function and identify the underlying cause. Accurate diagnosis is essential for determining the most appropriate management and treatment plan.
Medical Tests and Procedures
Here are some common tests and procedures used in the diagnosis of liver disease:
- Blood Tests: Liver function tests (LFTs) are a series of blood tests that measure the levels of enzymes and proteins in the blood. Elevated levels of liver enzymes, such as alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST), can indicate liver damage.
- Imaging Tests: Imaging tests, such as ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) scans, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), provide detailed images of the liver and can help identify abnormalities, such as tumors, cysts, or fatty liver.
- Liver Biopsy: A liver biopsy involves taking a small sample of liver tissue for examination under a microscope. It provides valuable information about the extent and type of liver damage, helping to confirm the diagnosis.
- FibroScan: This non-invasive test uses ultrasound technology to assess liver stiffness, which can indicate the presence of fibrosis or cirrhosis.
- Viral Hepatitis Tests: Specific blood tests can detect the presence of hepatitis viruses (A, B, C, D, and E) to determine if viral hepatitis is the cause of liver disease.
- Genetic Testing: Genetic testing may be recommended for individuals with a family history of liver disease or suspected genetic conditions, such as hemochromatosis or Wilson’s disease.
Technological Advancements in Diagnosis
Advancements in medical technology have significantly improved the accuracy and efficiency of liver disease diagnosis. Innovative techniques, such as elastography and advanced imaging modalities, have made non-invasive assessments more accessible and reliable.
These advancements not only enhance diagnostic accuracy but also reduce the need for invasive procedures, making the process more comfortable for patients. Early and accurate diagnosis is the cornerstone of effective management and treatment of liver disease, helping to minimise the impact on patients and healthcare systems.
Cost of Diagnosis
The financial implications of diagnosing liver disease can vary widely depending on the tests and procedures required. Understanding these costs is essential for individuals and healthcare systems alike.
Financial Implications of Diagnostic Tests
The cost of diagnosing liver disease can be a significant burden, particularly for individuals without insurance or access to affordable healthcare. Here are some factors that contribute to the overall cost:
- Blood Tests: While liver function tests are relatively inexpensive, additional tests, such as viral hepatitis screenings and genetic testing, can add to the cost.
- Imaging Tests: Imaging tests, such as ultrasounds and MRI scans, can be costly, especially if multiple tests are required for a comprehensive assessment.
- Liver Biopsy: Liver biopsy is an invasive procedure that can be expensive, especially when considering the costs of anesthesia and post-procedure care.
- Advanced Technology: Newer technologies, such as FibroScan and elastography, may come with higher costs due to their advanced capabilities.
Insurance and Accessibility
Access to affordable healthcare and insurance coverage plays a crucial role in determining the financial burden of diagnosing liver disease. Individuals with comprehensive health insurance are more likely to receive timely and cost-effective diagnostic care.
However, disparities in healthcare access can result in delayed or missed diagnoses, particularly for underserved populations. Addressing these disparities is essential for reducing the overall cost of liver disease on individuals and healthcare systems.
Management and Treatment Options
Once liver disease is diagnosed, effective management and treatment are essential for improving patient outcomes and quality of life. The approach to management depends on the specific type and stage of liver disease, as well as the underlying cause.
Lifestyle Changes and Medical Interventions
Lifestyle modifications and medical interventions are often the first steps in managing liver disease:
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthy lifestyle is crucial for managing liver disease. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and avoiding alcohol and illicit drugs. Weight management is particularly important for individuals with NAFLD.
- Medications: Depending on the underlying cause, medications may be prescribed to manage liver disease. For example, antiviral medications are used to treat chronic hepatitis B and C, while medications to reduce liver inflammation and fibrosis may be prescribed for NASH.
- Vaccinations: Vaccinations for hepatitis A and B are recommended to prevent these viral infections, which can worsen liver disease.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular monitoring of liver function and disease progression is essential for adjusting the treatment plan as needed.
Advances in Treatment Options
Advancements in medical research have led to the development of innovative treatment options for liver disease. For instance, new antiviral therapies for hepatitis C have significantly improved cure rates and reduced treatment duration.
In cases of liver failure or end-stage liver disease, liver transplantation may be considered. While transplantation can be life-saving, it comes with significant costs and requires long-term immunosuppressive therapy.
Cost of Treatment
The cost of treating liver disease can vary widely depending on the specific condition, severity, and treatment options chosen. It’s important to consider both the direct and indirect costs associated with treatment.
Comparing Treatment Costs
Here are some factors that contribute to the overall cost of treating liver disease:
- Medications: The cost of medications can vary depending on the type and duration of treatment. For example, antiviral medications for hepatitis C can be expensive, although prices have decreased in recent years.
- Hospitalisation and Procedures: Hospitalisation and procedures, such as liver biopsy or surgery, can add significantly to the cost of treatment.
- Liver Transplantation: Liver transplantation is one of the most costly treatments for liver disease, involving extensive medical and surgical expenses.
- Long-term Care: Chronic liver disease requires ongoing monitoring and management, which can result in cumulative costs over time.
Balancing Cost and Quality of Care
Balancing the cost of treatment with the quality of care is a challenge faced by both patients and healthcare providers. Ensuring access to affordable and effective treatment is essential for improving outcomes and reducing the overall burden of liver disease.
Healthcare systems must strive to provide cost-effective solutions that prioritise patient well-being while minimising financial strain. This includes increasing access to preventive measures, early diagnosis, and timely interventions.
Long-term Management and Follow-up
Long-term management and follow-up care are essential components of treating liver disease, particularly for chronic conditions. Regular monitoring and lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in preventing complications and improving quality of life.
Monitoring and Managing Chronic Liver Conditions
For individuals with chronic liver disease, regular monitoring is essential to assess disease progression and make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan. This includes:
- Regular Health Check-ups: Routine medical check-ups and liver function tests are essential for monitoring liver health and identifying any changes early.
- Imaging Studies: Periodic imaging studies, such as ultrasound or MRI, can help assess liver structure and detect any complications.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Ongoing lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding alcohol, are crucial for managing chronic liver conditions.
- Medication Adherence: Adhering to prescribed medications and treatment regimens is essential for controlling disease progression and preventing complications.
The Role of Regular Health Check-ups
Regular health check-ups are an important aspect of managing liver disease and preventing complications. They provide an opportunity for healthcare providers to assess liver function, monitor disease progression, and make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
In addition to medical interventions, individuals with liver disease can benefit from support and education to make informed decisions about their health. This includes understanding the importance of lifestyle modifications, recognising early warning signs of complications, and seeking timely medical attention.
Economic and Social Impact
Liver disease has a significant economic and social impact on individuals, families, and healthcare systems. Understanding these impacts is essential for developing effective strategies to address the burden of liver disease.
The Burden on Healthcare Systems
Liver disease places a substantial burden on healthcare systems worldwide. The costs associated with diagnosing, treating, and managing liver disease are significant, particularly for individuals with advanced or chronic conditions.
The economic impact of liver disease extends beyond direct medical costs, as it also affects productivity and workforce participation. Individuals with liver disease may experience reduced quality of life, increased absenteeism, and disability, all of which contribute to economic losses.
Impact on Patients and Families
Liver disease can have a profound impact on patients and their families, both financially and emotionally. The cost of medical care, combined with the need for long-term management and lifestyle changes, can be overwhelming for many individuals.
In addition to financial burdens, liver disease can affect the emotional and mental well-being of patients and their families. The uncertainty and challenges associated with managing a chronic condition can lead to stress, anxiety, and reduced quality of life.
Addressing the economic and social impact of liver disease requires a comprehensive approach that prioritises prevention, early detection, and effective management. This includes increasing access to healthcare services, improving patient education and support, and implementing policies that reduce the overall burden on individuals and healthcare systems.
Conclusion
Liver disease is a complex and multifaceted health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding the cost of liver disease involves more than just financial considerations; it encompasses the emotional, physical, and social impact on individuals and their families.
Early detection, accurate diagnosis, and effective management are essential for improving outcomes and reducing the overall burden of liver disease. This requires a collaborative effort from healthcare providers, policymakers, and individuals to prioritise prevention, increase access to care, and ensure that patients receive the support they need.
By taking a proactive approach to liver health, individuals can make informed choices about their lifestyle and health, ultimately reducing the risk of liver disease and improving their quality of life.
FAQs?
What are the early signs of liver disease?
Early signs of liver disease may include fatigue, jaundice, abdominal pain, nausea, and changes in urine and stool colour.
How is liver disease diagnosed?
Liver disease is diagnosed through a combination of blood tests, imaging studies, and sometimes a liver biopsy to assess liver function and identify the underlying cause.
Can liver disease be prevented?
Yes, liver disease can be prevented by adopting a healthy lifestyle, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, maintaining a balanced diet, and getting vaccinated against hepatitis.
What are the treatment options for liver disease?
Treatment options for liver disease vary depending on the underlying cause and may include lifestyle changes, medications, and, in severe cases, liver transplantation.
How much does liver disease treatment cost?
The cost of treating liver disease can vary widely depending on the specific condition, severity, and treatment options chosen. It can range from relatively low costs for lifestyle changes to high costs for liver transplantation.
What is the role of regular health check-ups in managing liver disease?
Regular health check-ups are essential for monitoring liver function, assessing disease progression, and making necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
How does liver disease affect individuals and families?
Liver disease can have a significant impact on individuals and families, both financially and emotionally, affecting quality of life, productivity, and mental well-being.