Heart disease, often dubbed the “silent killer,” remains one of the leading causes of death worldwide. But the impact of heart disease extends beyond health; it also imposes a significant financial burden on individuals, families, and healthcare systems. Understanding the costs associated with heart disease and the importance of prevention can save lives and reduce economic strain.
The financial ramifications of heart disease are staggering. Medical bills, loss of productivity, and the emotional toll on families are just a few of the costs involved. Prevention and management strategies are essential to mitigate these expenses. This article delves into the intricate web of costs associated with heart disease, the preventive measures that can make a difference, and how proactive management can lead to healthier lives and more sustainable healthcare systems.
The Financial Burden of Heart Disease
Some of the points you need to keep in mind for the financial burden of Heart Disease.
Direct Medical Costs
The direct medical costs of heart disease are extensive, encompassing hospital stays, surgeries, medications, and regular consultations with healthcare professionals. These costs can quickly increase, particularly for chronic conditions requiring long-term management. For many, the financial burden is exacerbated by the need for ongoing treatments and follow-ups.
Indirect Costs: Loss of Productivity and Earnings
Beyond the obvious medical expenses, heart disease often results in significant indirect costs. These include lost wages due to illness, reduced productivity, and the long-term economic impact of disability. Families and employers can feel the ripple effect, contributing to a broader economic burden.
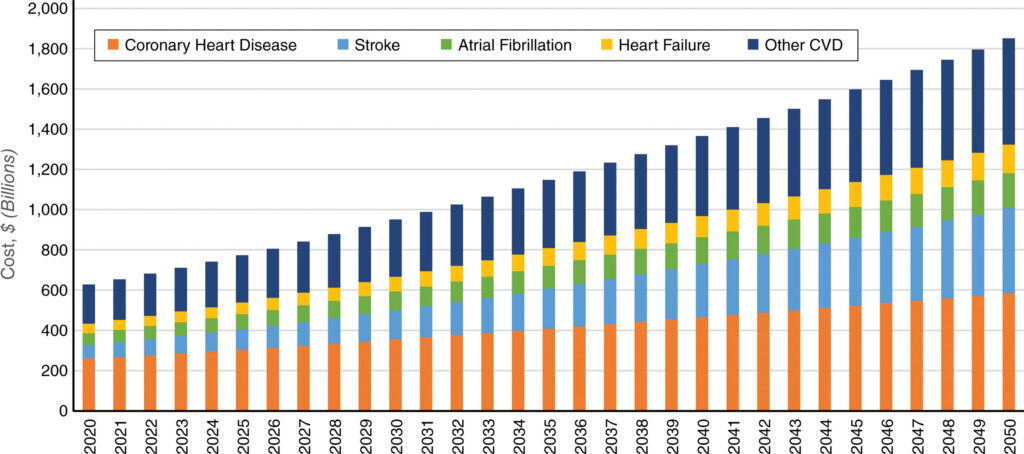
Factors Contributing to the High Costs
Healthcare Infrastructure and Services
The availability and quality of healthcare services play a crucial role in the overall cost of heart disease management. Regions with advanced healthcare infrastructure may offer better treatment options at a higher cost. Conversely, areas with limited access to healthcare can experience higher mortality rates and long-term costs due to delayed treatment.
Medication and Treatment Expenses
Medications for heart disease, including statins, blood thinners, and beta-blockers, can be costly, especially without insurance coverage. Surgical interventions, such as angioplasty and bypass surgery, are even more expensive, adding to the financial burden on patients and their families.
Impact on Families and Caregivers
The emotional and financial toll on families and caregivers is another significant factor. Providing care for someone with heart disease often requires time off work, which can lead to a loss of income. The stress and emotional strain can also have further health implications for caregivers.

Preventive Measures to Reduce Costs
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of heart disease through regular check-ups and screenings can significantly reduce long-term costs. Identifying risk factors early allows for timely intervention, which can prevent the progression of the disease and the need for more expensive treatments later.
Lifestyle Changes and Their Impact
Simple lifestyle changes can have a profound impact on heart disease prevention. Adopting a healthier diet, increasing physical activity, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption are all effective strategies. These changes improve heart health and reduce the healthcare costs associated with treating advanced heart disease.
Role of Regular Check-ups
Regular medical check-ups are vital for monitoring heart health and detecting potential issues early. Consistent monitoring can help manage risk factors such as high blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes, which are all significant contributors to heart disease.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Balanced Diet and Nutrition
A heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is essential for preventing heart disease. Reducing the intake of saturated fats, trans fats, and sodium can lower the risk of cardiovascular disease. Embracing a balanced diet benefits heart health and enhances overall well-being.
Physical Activity and Exercise
Regular physical activity is a cornerstone of heart disease prevention. Exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, reduces blood pressure, and improves cholesterol levels. Walking, jogging, cycling, and swimming are excellent for cardiovascular health and can be easily incorporated into daily routines.
Avoiding Tobacco and Limiting Alcohol
Smoking is a major risk factor for heart disease. Quitting smoking and avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke can dramatically reduce heart disease risk. Additionally, limiting alcohol consumption to moderate levels is crucial, as excessive drinking can lead to high blood pressure and other heart-related problems.

Medical Management of Heart Disease
Medications and Their Costs
Effective management of heart disease often requires a combination of medications. While these drugs are essential for controlling symptoms and preventing complications, their costs can be substantial. Patients must work closely with healthcare providers to find the most cost-effective treatment plans.
Surgical Procedures and Hospital Stays
For many patients, surgical interventions such as angioplasty, stenting, or coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) are necessary. These expensive procedures usually require extended hospital stays, further increasing the financial burden. Post-surgical care and rehabilitation add to these costs, making comprehensive insurance coverage crucial.
Rehabilitation and Long-term Care
Cardiac rehabilitation is a critical component of recovery for heart disease patients. This involves supervised exercise, education, and counseling to help patients regain their health and prevent future cardiac events. Long-term care and support services are also necessary for many, particularly those with severe heart conditions, adding to the overall cost of management.
Government and Community Initiatives
Public Health Campaigns
Governments and health organisations play a vital role in heart disease prevention through public health campaigns. These initiatives raise awareness about risk factors, promote healthy lifestyles, and provide information on early detection and treatment options. Effective campaigns can lead to behavioral changes that significantly reduce the incidence of heart disease.
Access to Affordable Healthcare
Ensuring access to affordable healthcare is essential for managing heart disease effectively. Policies that provide coverage for preventive services, medications, and treatments can alleviate the financial burden on individuals and families. Community health programs that offer free or low-cost screenings and check-ups are also beneficial.
Support Groups and Resources
Support groups and resources for heart disease patients and their families are invaluable. These groups provide emotional support, practical advice, and disease management information. They can also advocate for better healthcare policies and services, contributing to improved patient outcomes.
Technological Advances in Heart Disease Management
Innovative Treatments and Devices
Technological advancements have revolutionised heart disease treatment. These innovations, from minimally invasive surgical techniques to advanced diagnostic tools, have improved patient outcomes and reduced recovery times. Devices such as pacemakers, defibrillators, and heart pumps are increasingly sophisticated, providing better management options for patients.
Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring
Telemedicine has emerged as a valuable tool in managing heart disease, particularly for patients in remote or underserved areas. Remote monitoring devices allow healthcare providers to track patients’ heart health in real time, enabling timely interventions and reducing the need for frequent hospital visits.
Research and Development
Ongoing research and development are crucial for advancing heart disease treatment and prevention. Clinical trials and studies help discover new medications, therapies, and disease management approaches. Investment in research can lead to breakthroughs that significantly reduce the incidence and impact of heart disease.
Insurance and Financial Planning
Importance of Health Insurance
Having comprehensive health insurance is vital for managing the costs associated with heart disease. Insurance can cover significant medical expenses, including hospital stays, surgeries, and medications. It also provides access to preventive services to help detect and address risk factors early.
Planning for Unexpected Medical Costs
Financial planning is essential for managing unexpected medical costs. Setting aside funds for emergencies and understanding insurance coverage can help individuals and families navigate the financial challenges posed by heart disease. Consulting with financial advisors can also provide strategies for managing healthcare expenses effectively.
Financial Assistance Programs
Various financial assistance programs are available to help heart disease patients manage their medical expenses. These programs can fund treatments, medications, and other necessary services. Patients should explore these options and seek assistance from healthcare providers or social workers to find the support they need.
Conclusion
Heart disease imposes a significant financial burden on individuals, families, and healthcare systems. However, these costs can be mitigated through proactive prevention and effective management. Early detection, lifestyle changes, and access to affordable healthcare are key strategies in reducing the impact of heart disease. Embracing these measures improves heart health and contributes to a more sustainable and efficient healthcare system.
Frequently Asked Questions?
What are the common symptoms of heart disease?
Common symptoms of heart disease include chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, palpitations, and dizziness. It is important to seek medical advice if you experience these symptoms.
How can I reduce my risk of heart disease?
You can reduce your risk of heart disease by maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, avoiding tobacco, limiting alcohol consumption, and managing stress. Regular check-ups and monitoring of blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels are also crucial.
Are there affordable treatment options for heart disease?
Yes, there are affordable treatment options for heart disease, including generic medications, community health programs, and financial assistance programs. It is essential to discuss all available options with your healthcare provider.
What role does diet play in preventing heart disease?
Diet plays a significant role in preventing heart disease. A heart-healthy diet includes many fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Reducing the intake of saturated fats, trans fats, sodium, and added sugars is also important.
How can I support a loved one with heart disease?
Supporting a loved one with heart disease involves offering emotional support, helping with medical appointments, encouraging healthy lifestyle changes, and providing practical assistance with daily activities. Joining support groups and staying informed about the condition can also be helpful.
What are the latest advancements in heart disease treatment?
Recent advancements in heart disease treatment include minimally invasive surgical techniques, advanced diagnostic tools, innovative medications, and remote monitoring technologies. These advancements improve patient outcomes and reduce recovery times.
How important is regular exercise in heart disease prevention?
Regular exercise is crucial in preventing heart disease. It helps maintain a healthy weight, lowers blood pressure, improves cholesterol levels, and reduces stress. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity each week and muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days a week.